It is used to retrieve data that contains a character or subset of characters in a character set, or to check data that satisfies conditions in a set of data. Don’t get confused, you will understand very well with examples.
LIKE Operator
For example, let’s take the authors with the b character in the name;
SELECT * FROM company WHERE name LIKE '%B%'

The point we need to pay attention to here is that it doesn’t matter if it is lowercase or uppercase.
The
%character is used to indicate that the character is a wildcard.
Now let’s find the names that start with the character A;
SELECT * FROM company WHERE name LIKE 'A%'

Now let’s find the name with 5 characters;
SELECT * FROM company WHERE name LIKE '_____'
Now let’s find the name with 5 characters whose second character is O;
SELECT * FROM company WHERE name LIKE '_O___'

Let’s do another example, let’s write the name that starts with B and ends with L;
SELECT * FROM company WHERE name LIKE 'B%L'

IN Operator
If it satisfies any of the given values.
SELECT * FROM company WHERE department_no IN (10, 12)
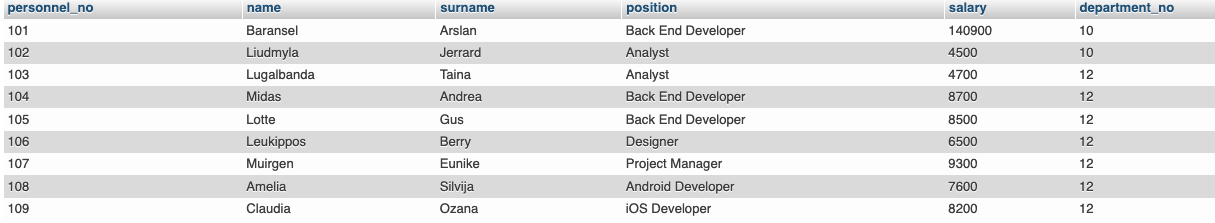
Let’s do another example. This time, let’s find authors with 8 characters whose last letter ends with L and authors whose department number is 10 or 12.
SELECT * FROM company WHERE name LIKE '_______L' AND department_no IN (10, 12)
